
Kim Lien Temple
Kim Lien Temple
VIETNAM, Hanoi
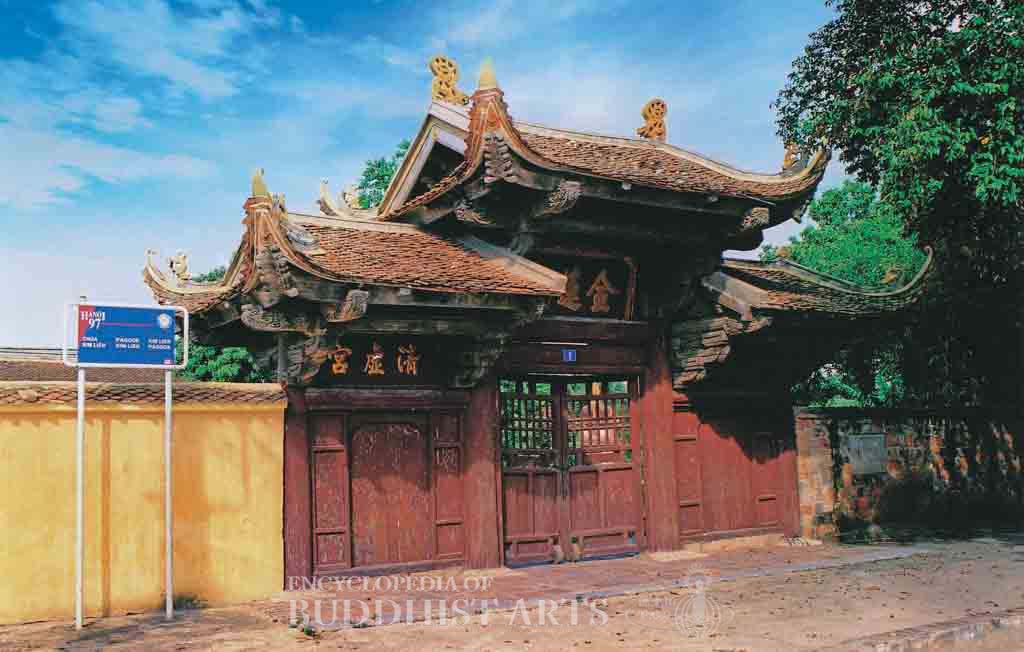
Kim Lien means Golden Lotus. The temple was built in 1443 and repaired in 1771, when it was given its current name. It has been restored a number of times and was reconstructed in 1980 and 2000. It is listed as a National Cultural Heritage Site.
The principal buildings include the main temple gate, main hall, lecture hall, and reception hall. The main temple gate is three bays wide, with the central bay taller than the side bays. Each bay has its own hip-and-gable roof with corners curving upward. The main hall has a double-eave hip-and-gable roof and circular windows. The bracket sets within the hall are carved in various designs, such as clouds and dragon heads. The lecture hall and reception hall are side halls behind the main hall. The temple contains images of Amitabha Buddha and Avalokitesvara, Mahasthamaprapta, Samantabhadra, and Manjusri Bodhisattvas, which were produced between the 17th and 19th centuries.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 607.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 607,
title = {{Kim Lien Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}