
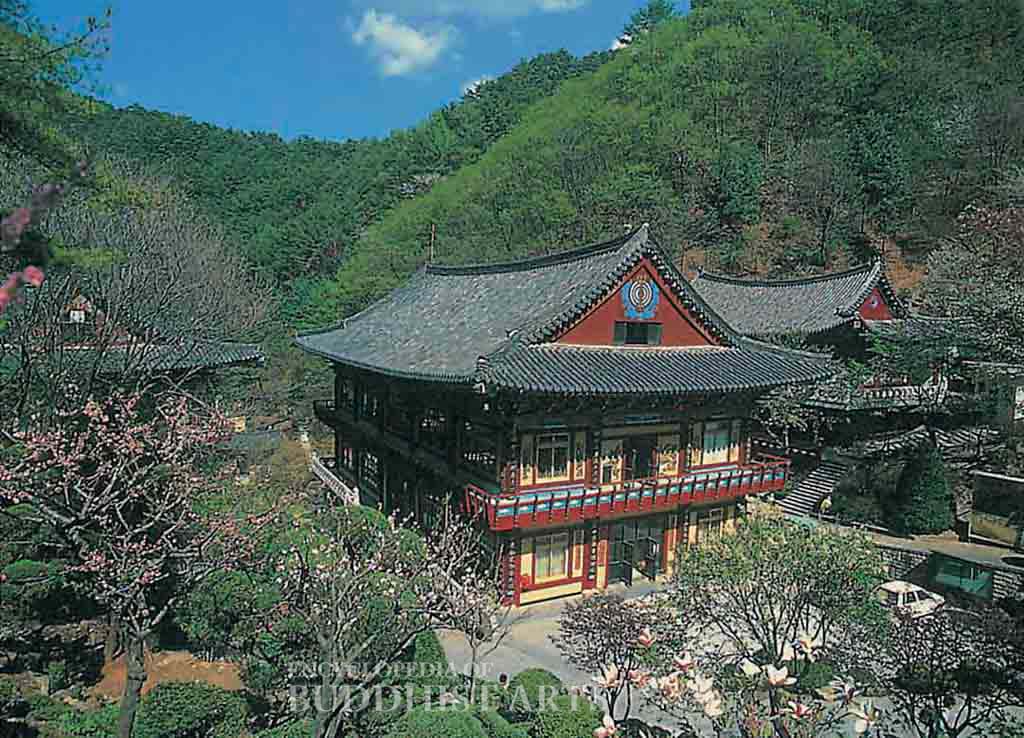
Guinsa Temple (aerial view)

Guinsa Temple
Guinsa Temple
SOUTH KOREA, North Chungcheong, Danyang
Guinsa, or Temple of Salvation and Kindness, is located within the National Park of the Sobaek Mountains. It was established in 1945 by monk Sangwol Wongak and is the headquarters of the Cheontae school of Korean Buddhism.
The temple complex is built along a mountain valley and occupies 9,917 sq m. The temple consists of more than 50 buildings, including the Great Dharma Hall, Gate of the Four Heavenly Kings, and three-tier stone pagoda. The architecture of the temple is special because its buildings consist of several stories, instead of the typical one or two stories in most Korean temples. Most of the structures are decorated with the symbol of the vajra, which represents the ability to drive away the troubles of all living beings.
The Gate of the Four Heavenly Kings occupies nearly 200 sq m and has the largest bronze statues of the Four Heavenly Kings. The 33 m high Great Dharma Hall is the main building of the temple and can accommodate more than 1,000 people. It consists of five stories, with meditation halls on the first and second stories, and shrines on the third and fourth stories. On the fifth story there is a large Dharma Hall housing a statue of Sakyamuni Buddha, flanked by Avalokitesvara and Mahasthamaprapta Bodhisattvas.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 413.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 413,
title = {{Guinsa Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}