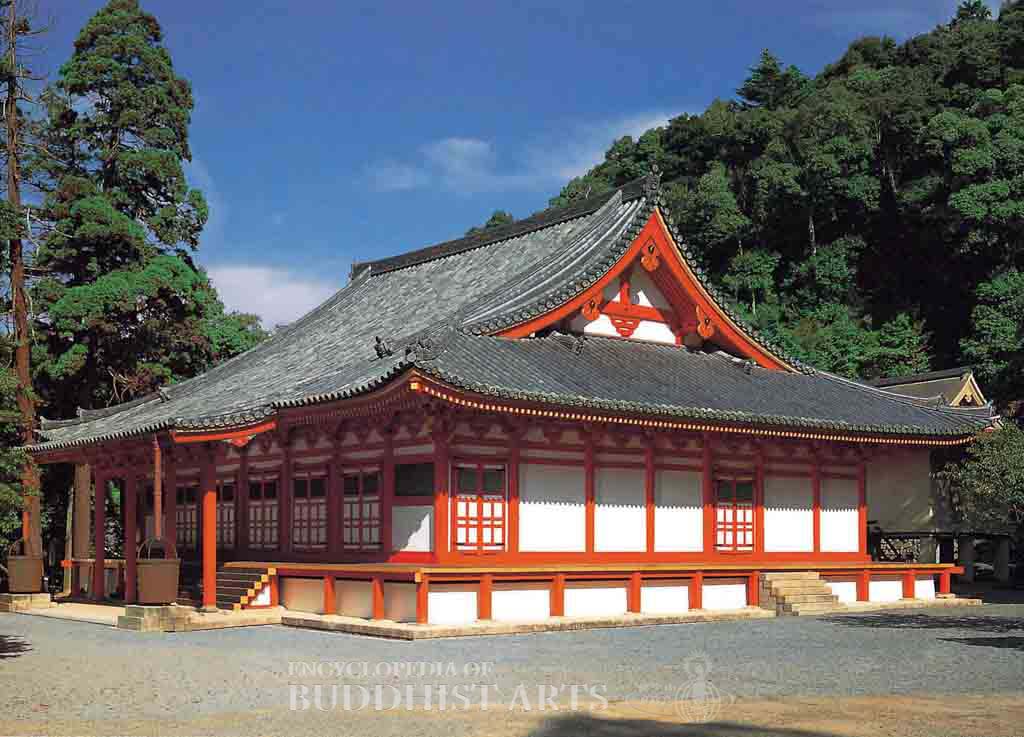

Kanshinji Temple: Golden Hall
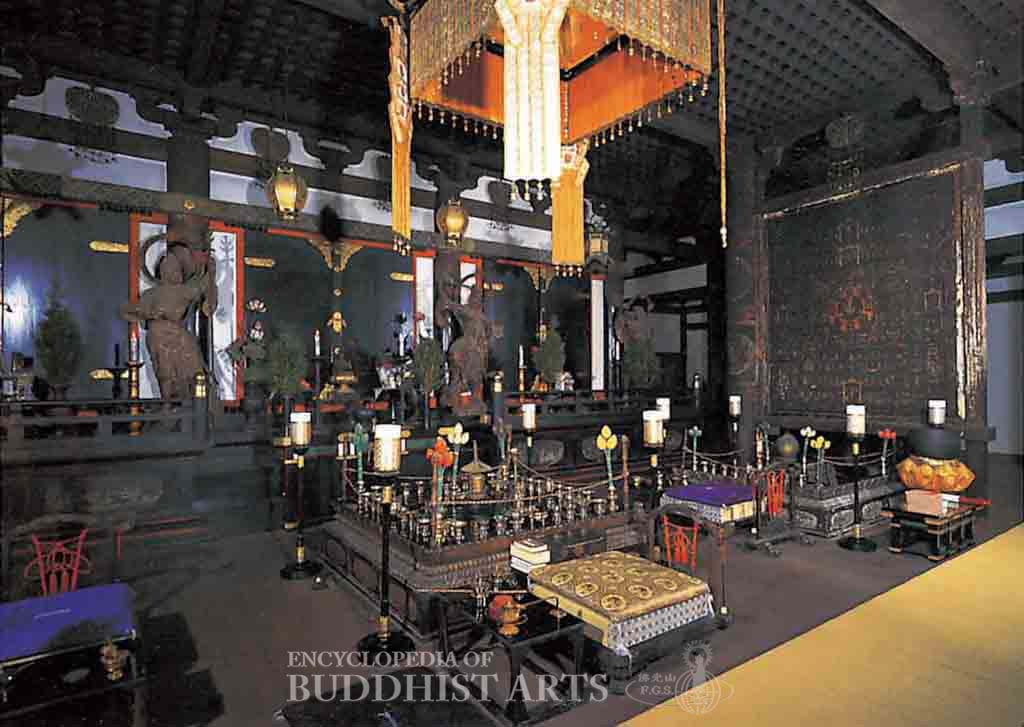

Kanshinji Temple: Golden Hall (interior)
Kanshinji Temple
JAPAN, Osaka, Kawachinagano
This temple is located on Mount Koya and belongs to the Shingon school of Japanese Buddhism. It was established in 701 by Enno Ozuno and underwent a number of name changes. It received royal patronage during the time of Emperor Saga (reigned 809–823), was listed as an official temple in 869, and became a state-sponsored temple under Emperor Go-Daigo (reigned 1318–1339). It has been damaged and repaired a number of times throughout its history.
The main buildings are the temple gate, Golden Hall, founder’s hall, unfinished pagoda, Hariti Hall and study room. The seven-by-seven bay Golden Hall, listed as a National Treasure in 1952, was built between 1346 and 1370 during the Nanbokucho period. It has a single-eave hip-and-gable roof covered in cylindrical tiles. The roof is extended at the front to provide additional worshipping space. The overall appearance is that of a series of vertical and horizontal red lines against a white background. Statues of Cintamanicakra Avalokitesvara flanked by Acala and Ragaraja are enshrined on a platform within the hall. On the opposite side are statues of the Four Heavenly Kings from the Heian period (794–1185). On either side of the altar screen, there are paintings of the Diamond Realm Mandala and Womb Realm Mandala. There are Vajrayana Buddhist Dharma instruments in the central area. The hall is a representative of the Shingon tradition.
The founder’s hall was built in the early Edo period (1615–1868). It has a pyramidal roof covered with cypress bark. The unfinished pagoda was begun by General Kusunoki Masashige during the Muromachi period (1392–1573) but was left incomplete after his death in battle. It has a pyramidal roof supported by three-tier bracket sets, and a statue of Vairocana Buddha is enshrined inside the building.
The temple houses Important Cultural Properties, including the painting of Mahapratisara Bodhisattva, as well as statues of an eminent monk, Eleven-Headed Avalokitesvara, and Maitreya Buddha.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 589.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 589,
title = {{Kanshinji Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}