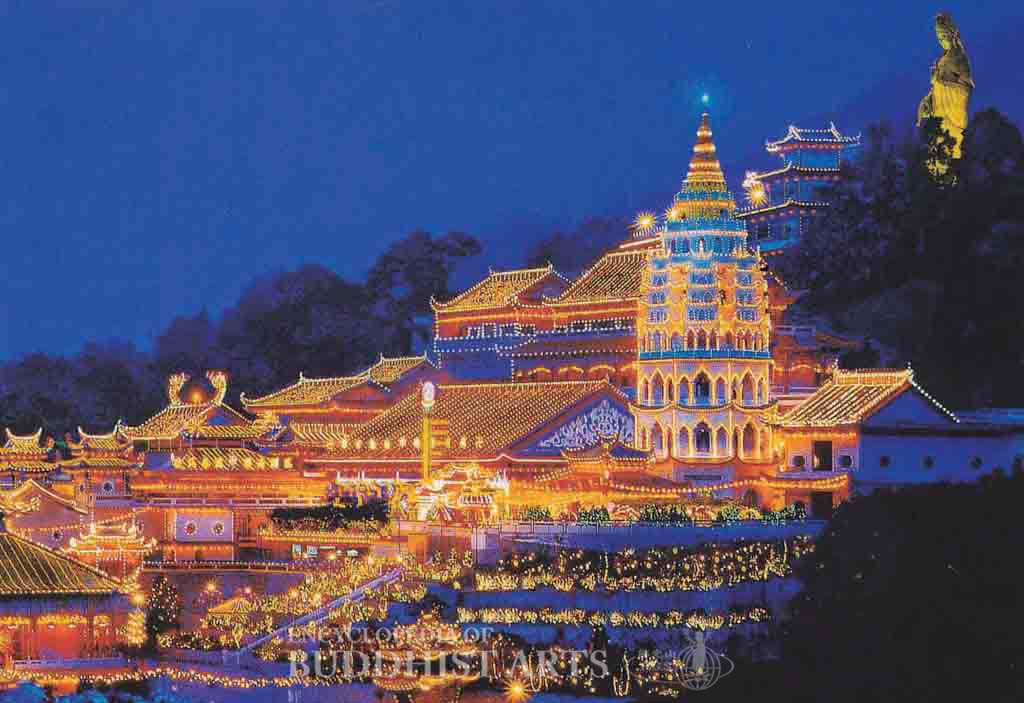

Kek Lok Si Temple
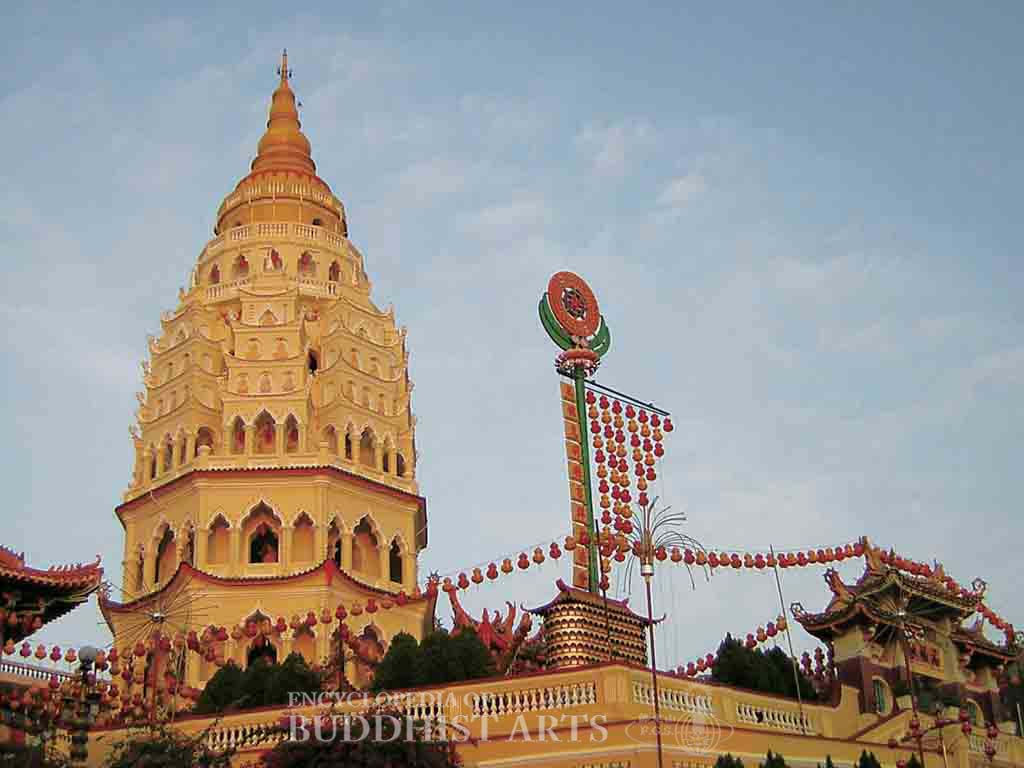

Kek Lok Si Temple: Ten Thousand Buddha Pagoda
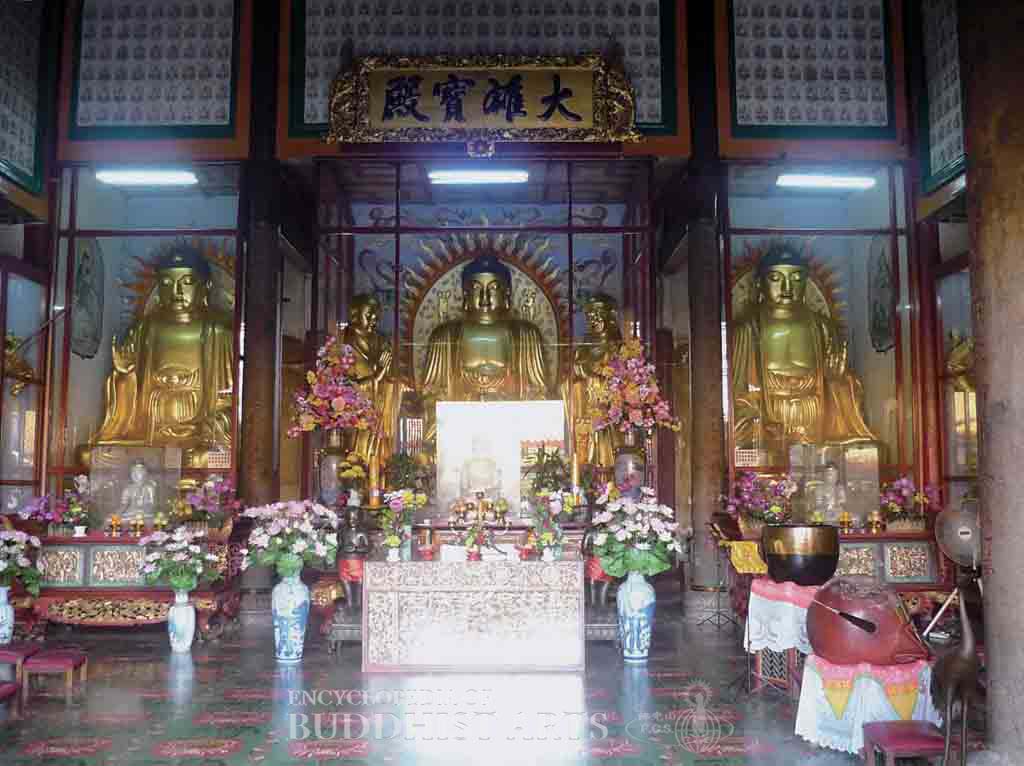

Kek Lok Si Temple: Great Hero Hall (interior)
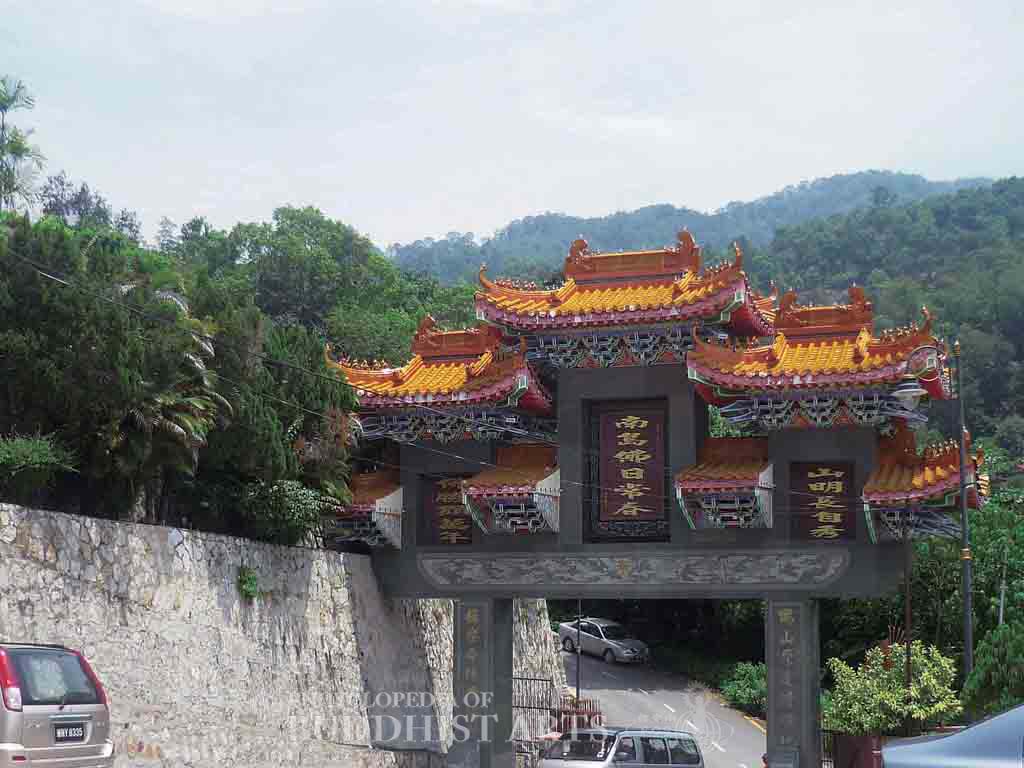

Kek Lok Si Temple: Main Temple Gate
Kek Lok Si Temple
MALAYSIA, Penang, Air Itam
The temple was founded in 1891 by Fujianese monk Beow Lean and is considered to be one of the finest Mahayana Buddhist temples in Southeast Asia.
The temple occupies 12.1 ha and is built on a slope. It consists of the main temple gate, Bodhisattva Hall, Great Hero Hall, Heavenly King Hall, Dharma Hall, Hall of the Five Dhyani Buddhas, the Ten Thousand Buddha Pagoda, Amitabha Pagoda, the First Turning of Dharma Wheel Park, Sangharama Hall, Ksitigarbha Hall, and bell and drum towers. At the top of the hill there is a statue of Avalokitesvara Bodhisattva.
The oldest building is the Bodhisattva Hall, which has a double-eave hip-and-gable roof and houses the Bodhisattvas Avalokitesvara, Samantabhadra, and Manjusri. The Great Hero Hall emulates that of Yongquan Temple in Fuzhou, China, and is an important example of the southern Fujianese style of architecture. Behind the Great Hero Hall there is the three-story Dharma Hall, which contains a sutra repository on its top story and a library on the lower stories. The Ten Thousand Buddha Pagoda is nine stories high and displays an eclectic mix of Chinese, Thai, and Burmese architecture. Several Buddha statues in the Chinese, Burmese, and Thai traditions are enshrined within the pagoda. The construction of the 36.5 m high bronze statue of Avalokitesvara Bodhisattva started in 1974 and was completed in 2002. It is the tallest Avalokitesvara statue in Malaysia. At the base of the statue is the Yuan Tong Assembly Hall, which can accommodate up to 5,000 people. Outside the shrine there is a stone wall engraved with the Heart Sutra, a stone lion, a stone elephant, heavenly beings, and various Buddhist figures.
The temple has a collection of valuable historical artifacts, such as gifts from Emperor Guangxu (reigned 1875–1908) of the Qing dynasty, including two horizontal inscribed boards and the Qing Tripitaka in 8,000 fascicles. Also present are examples of texts written by Empress Cixi, as well as calligraphy, stone inscriptions, and column couplets by Kang Youwei, the king of Thailand, and other famous people. Items belonging to the founder monk Beow Lean include his staff and sutras written in his blood. The documents are an important source for research on the history of Chinese Buddhist culture and art in the region.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 597.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 597,
title = {{Kek Lok Si Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}