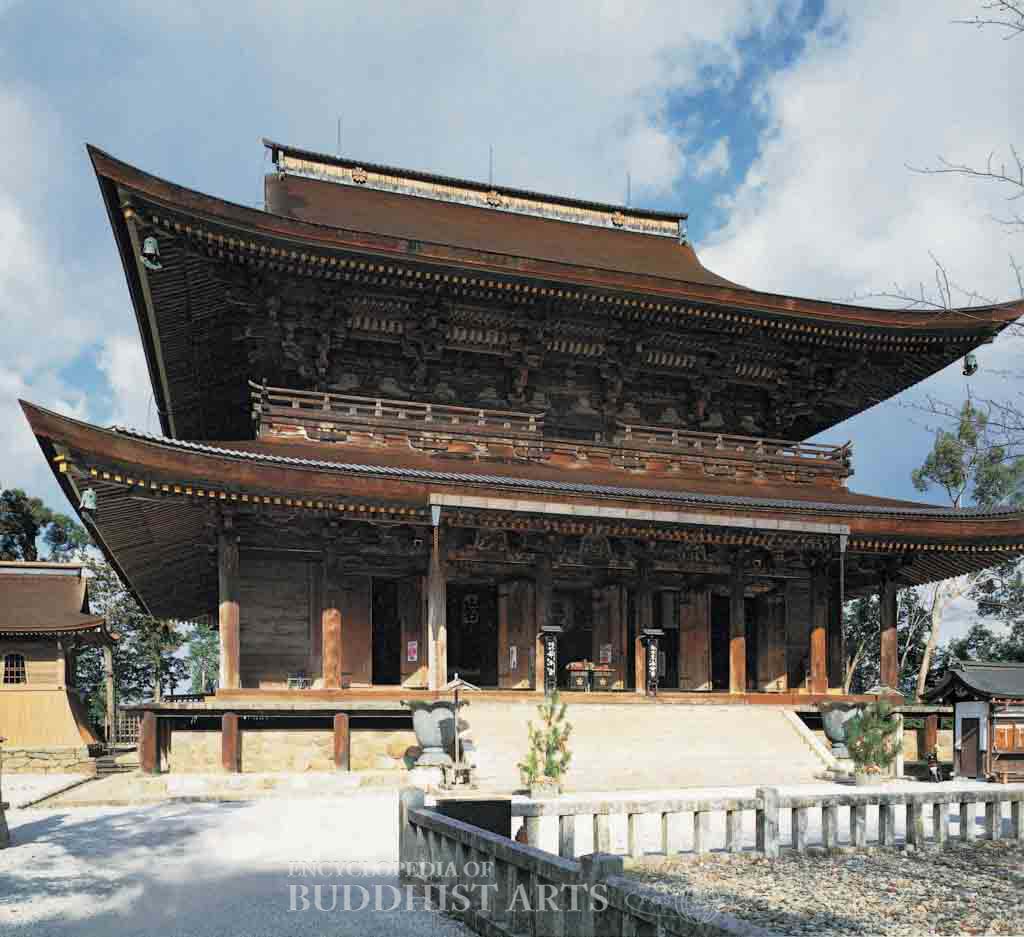

Kinpusenji Temple: Main Hall

Kinpusenji Temple: Gate of Benevolent Kings
Kinpusenji Temple
JAPAN, Nara, Yoshino
Kinpusenji is located on Mount Yoshino at 364 m above sea level and is the head temple of the Shugendo school. It was established by En no Ozunu in 672 during the Hakuho period. The Shugendo school draws upon Buddhist and Shinto beliefs and became popular, with more than a hundred temples scattered around Kinpusen and the foothills and summit of Mount Yoshino. During the late Heian period (794–1185), the temple enjoyed the same reputation as Kongobuji Temple on Mount Koya, with the increasing popularity of Vajrayana Buddhism and the participation of royalty. During the Nanbokucho period (1336–1392), the temple became the temporary residence of Emperor Go-Daigo (reigned 1318–1339). During the early Meiji period (1868–1912), when Shinto and Buddhism were separated, the temples were converted to Shinto shrines and thus were able to survive. In 1886, the temple reverted to being a Buddhist temple. The main hall is now the center of the Shugendo school.
The principal buildings include the gateway, Gate of Benevolent Kings, main hall, Avalokitesvara Hall, Ragaraja Hall, and bell tower. The main hall and the Gate of Benevolent Kings were designated National Treasures in 1953. The gateway was reconstructed during the Muromachi period (1392–1573). The three-bay wide Gate of Benevolent Kings has a double-eave hip-and-gable roof covered in cylindrical tiles. The 13.4 m high gate has statues of the benevolent kings situated on either side of the doorway. The main hall has a double-eave hip-and-gable roof covered with cypress bark. The building is 25.8 m wide and 27.7 m high. There are columns, 1 m in diameter, on the first story with camel-hump braces and flower-shaped bracket sets at the capitals. There are low balustrades on the second story and four-tier bracket sets under the eaves. Within the hall there is a cabinet as high as the ceiling housing a statue of Vajragarbha Bodhisattva. The temple houses several excavated artifacts from the Heian period, which are listed as National Treasures.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 607.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 607,
title = {{Kinpusenji Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}