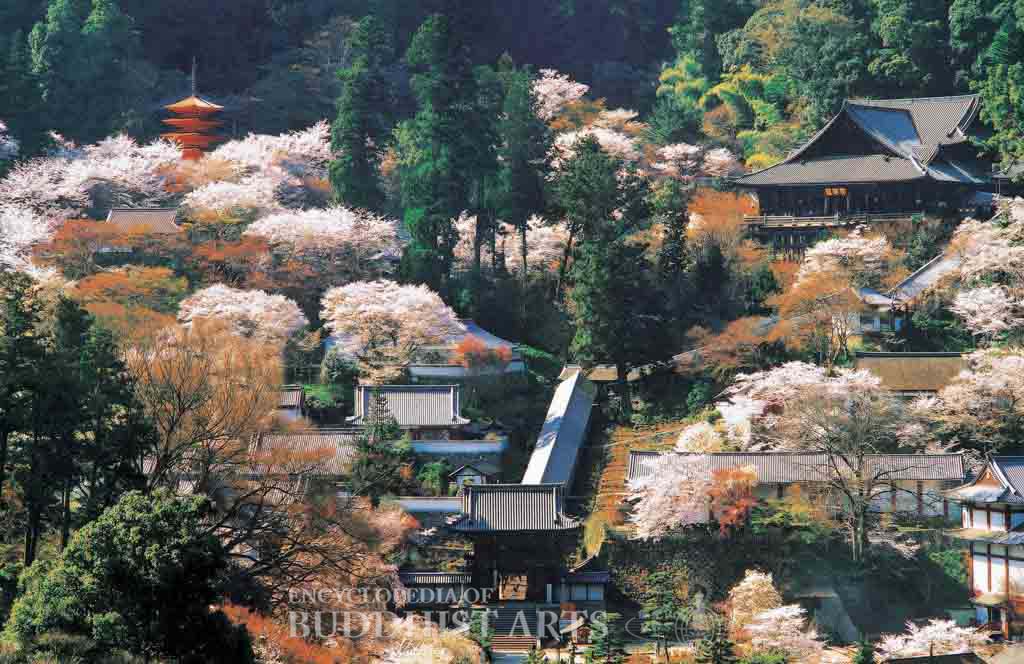

Hasedera Temple
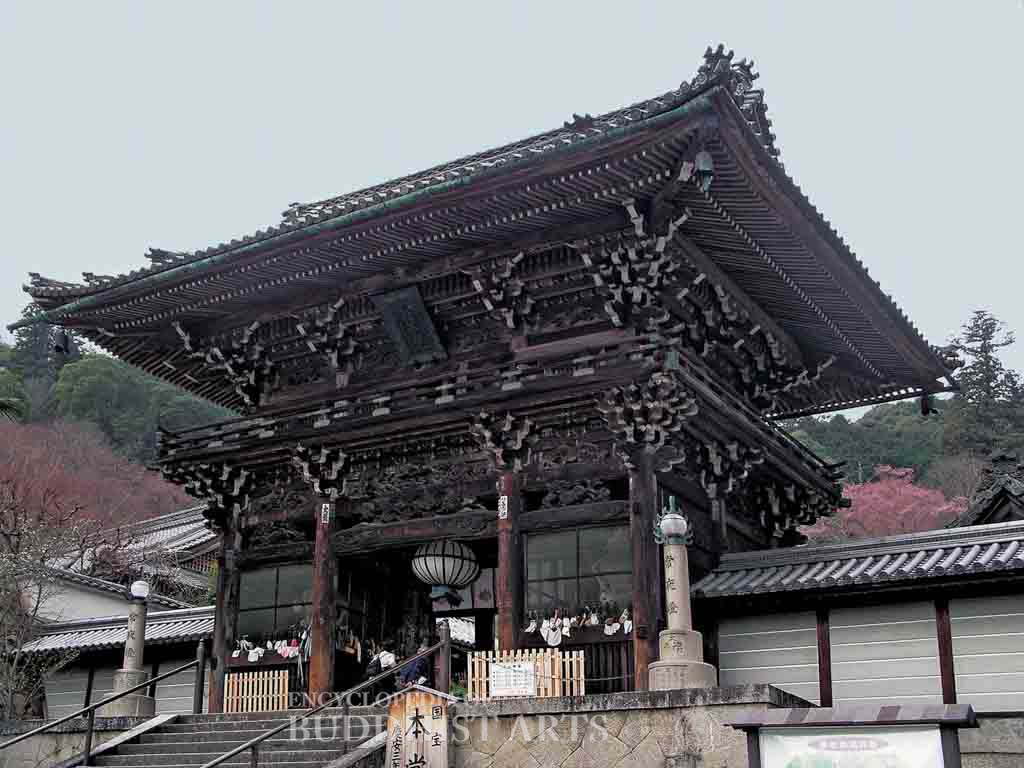

Hasedera Temple: Benevolent King Gate
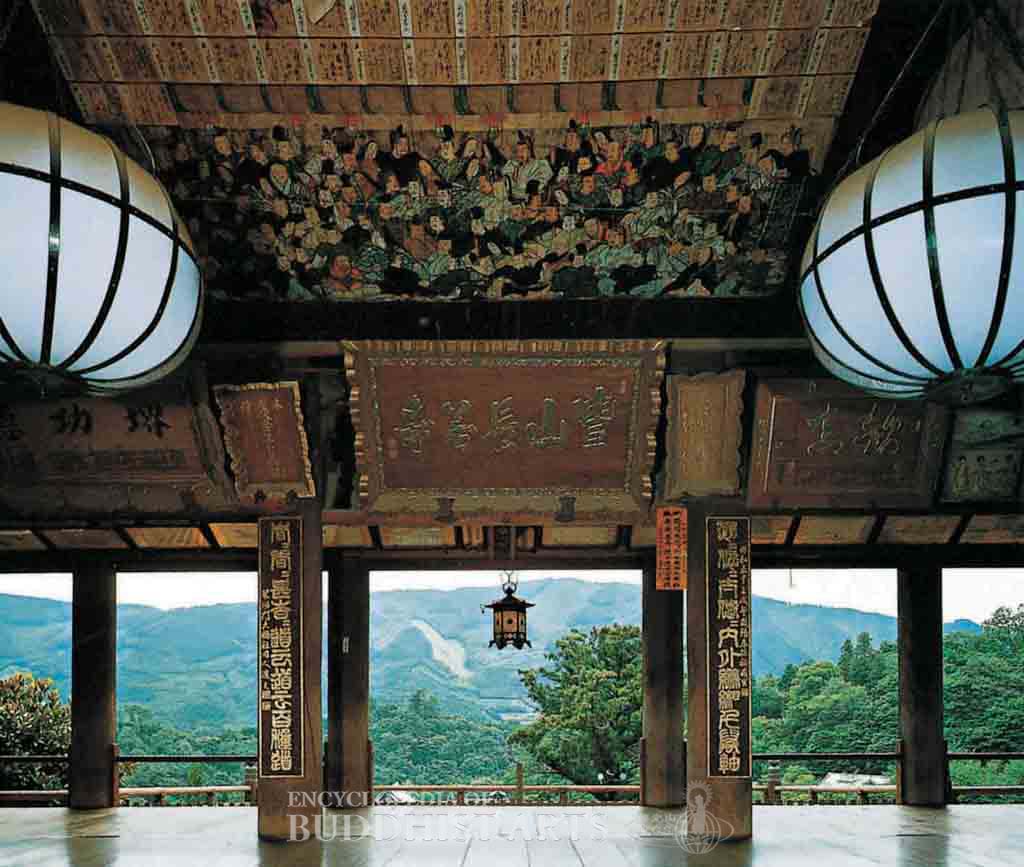

Hasedera Temple: Main Hall
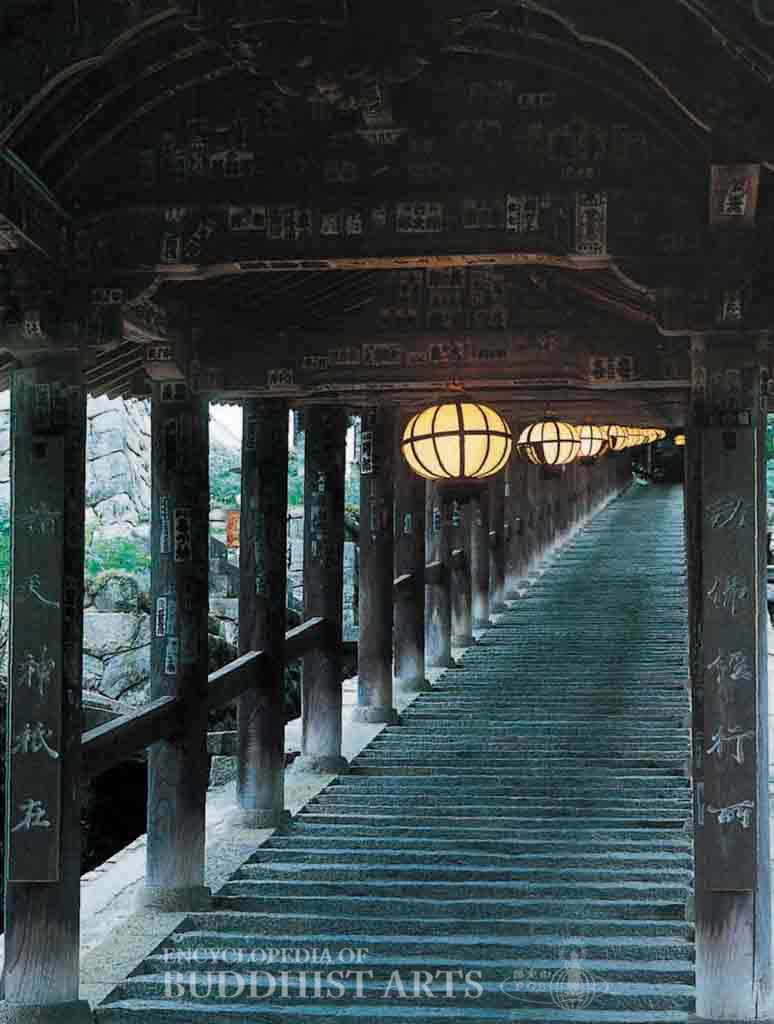

Hasedera Temple: Ascending Walkway
Hasedera Temple
JAPAN, Nara, Sakurai
Hasedera is the head temple of the Buzan branch of the Shingon school of Japanese Buddhism. It is the 8th of the 33 Avalokitesvara temples of the Saigoku Kannon Pilgrimage of southern-central Japan. The temple was likely founded in 686 during the Hakuho period by monk Domyo, who built a pagoda where he installed a plaque with illustration of the Lotus Sutra. The temple gradually deteriorated and was rebuilt in 1583 during the Azuchi-Momoyama period. The current temple was reconstructed in 1650 during the Edo period with the support of Tokugawa Iemitsu.
The temple follows the contours of the mountainside around it. The main structures include the main hall, the Mahakala Hall, founder’s hall, five-story pagoda, Gate of Benevolent Kings, ascending walkway, bell tower and lecture hall. The main hall was listed as a National Treasure in 2004, while the Gate of Benevolent Kings, ascending walkway, and bell tower were listed as Important Cultural Properties in 1986.
The nine-by-nine bay main hall is 25.9 m wide and 27 m deep with a hip-and-gable roof covered in cylindrical tiles. This complex structure, only second in size to the Golden Hall at Todaij Temple, is one of the most famous buildings from the Edo period (1615–1868). Inside the hall there is a wooden statue of the Eleven-Headed Avalokitesvara Bodhisattva. The statue is an Important Cultural Property and is the largest wooden sculpture in Japan with a height of more than 10 m.
The 27 m high five-story pagoda was built in 1954 during the Showa period. It is painted in vermilion red and its roof is covered with cypress bark. The Gate of Benevolent Kings serves as the main temple gate. It was rebuilt in 1885 during the Meiji period. The two-story gate has a horizontal board inscribed with the temple name written by Emperor Go-Yozei (reigned 1586–1611). Statues of the Benevolent Kings are placed on the first story, while the second story has statues of the Sakyamuni Buddha Triad and the Sixteen Arhats. The ascending walkway has 399 steps and a length of 200 m. The temple houses artifacts such as the image of the Water-Moon Avalokitesvara, an incense burner, the frontispiece of the “Chapter on Peaceful Practices” in the Lotus Sutra, and a wooden sutra box.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 431.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 431,
title = {{Hasedera Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}