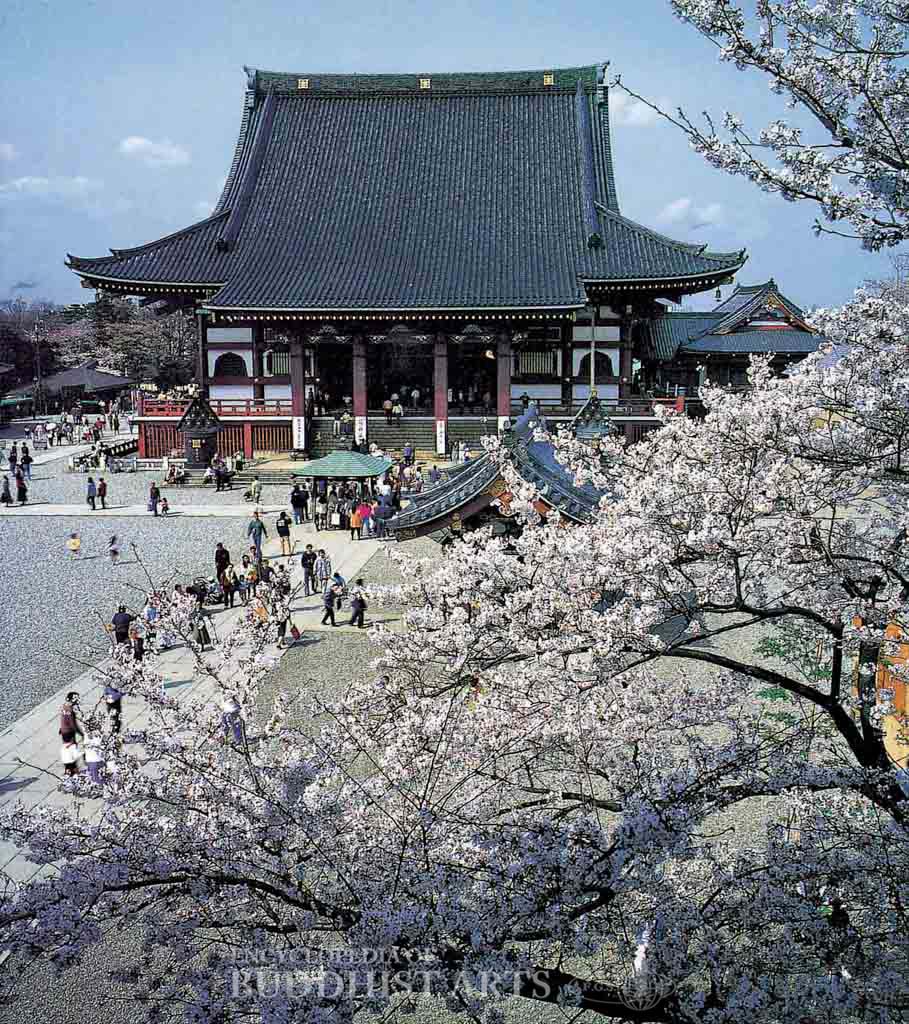

Honmonji Temple: Great Hall
Honmonji Temple
JAPAN, Tokyo
The temple was built on 23.14 ha of land donated by Master Nichiren in 1282 during the Kamakura period. It is one of the three major temples of the Nichiren school of Buddhism. The temple has been destroyed and rebuilt a number of times and most of the present buildings were reconstructed following heavy wartime damage in 1945.
The main buildings include the Gate of Benevolent Kings, Great Hero Gate, great hall, main hall, great reception hall, octagonal hall, Precious Spirit Hall, Nichiren Shrine, sutra repository, bell tower, funerary stupa, and five-story pagoda, which was listed as an Important Cultural Property in 1911. The Gate of Benevolent Kings was completed in 1977 during the Showa period. It has a height of 17.2 m and is built of steel and cement, with a roof made of cylindrical tiles. The 18-by-19 bay great hall was built in 1964 as a patriarch hall. It is approximately 28 m high and has a single-eave hip-and-gable roof. The five-story pagoda was built in 1608 during the Azuchi-Momoyama period. It is 31 m high and is the oldest wooden pagoda in Tokyo. The funerary stupa is dedicated to Nichiren and was constructed in 1830 during the Edo period. It is a 17.5 m high wooden structure with copper tiles.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 454.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 454,
title = {{Honmonji Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}