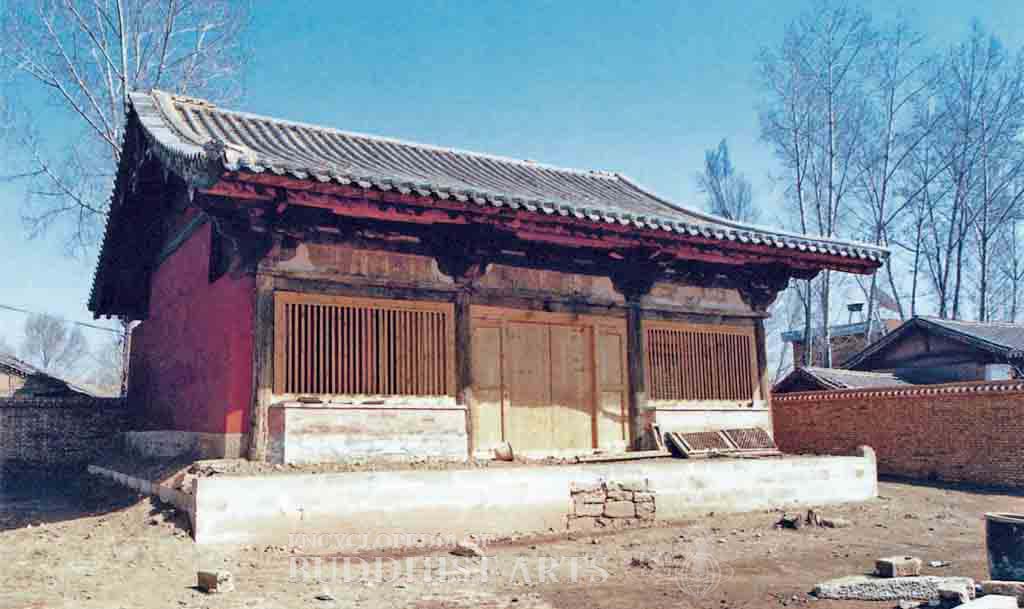

Dayun Yuan Temple: Main Hall
Dayun Yuan Temple
CHINA, Shanxi, Changzhi
The construction date of the temple is unknown but it does have a horizontal inscribed board dating to 1212 during the Jin dynasty. Reconstructions and renovations were carried out during the Ming (1368–1644) and Qing (1644–1911) dynasties. It was listed as a National Cultural Heritage Site in 2001.
The temple faces south and occupies an area of 927.2 sq m. It consists of one courtyard and only the main temple gate and the main hall are extant. The three-by-two bay main temple gate has a single-eave overhanging gable roof and appears to be in Qing dynasty style. The main hall occupies an area of 183.6 sq m and is a three-bay by six-rafter structure with a single-eave overhanging gable roof. The capitals of the columns support single-tier bracket sets with carvings of tripartite brackets featured in between.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture A-F, page 223.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture A-F},
pages = 223,
title = {{Dayun Yuan Temple}},
volume = 1,
year = {2016}}