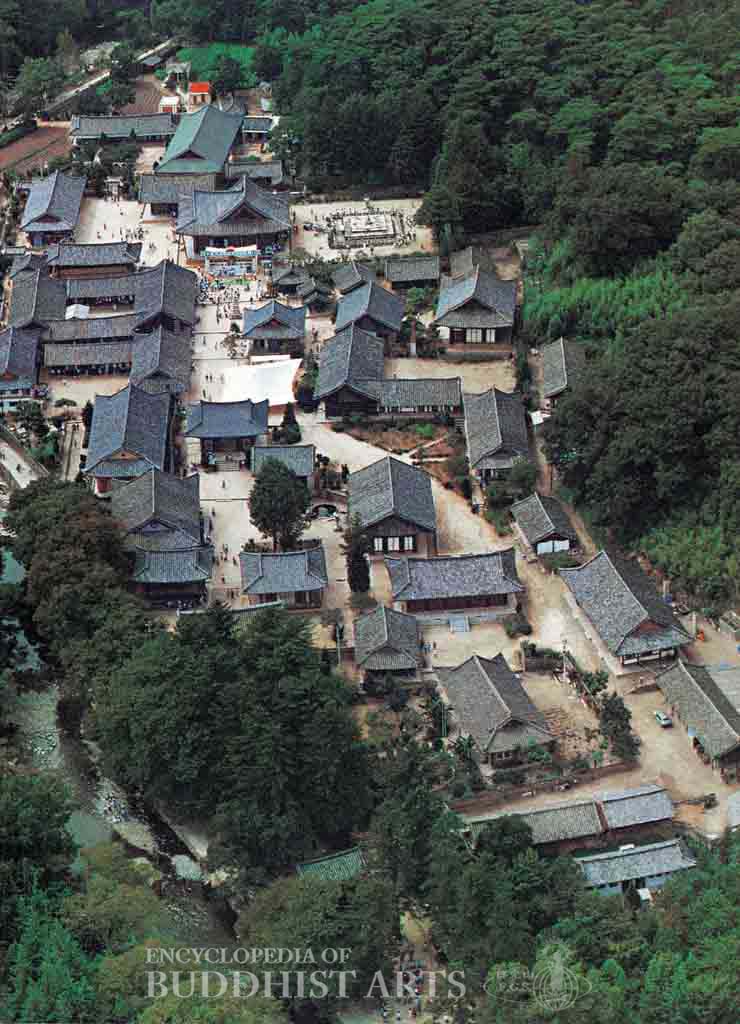

Tongdosa Temple (aerial view)
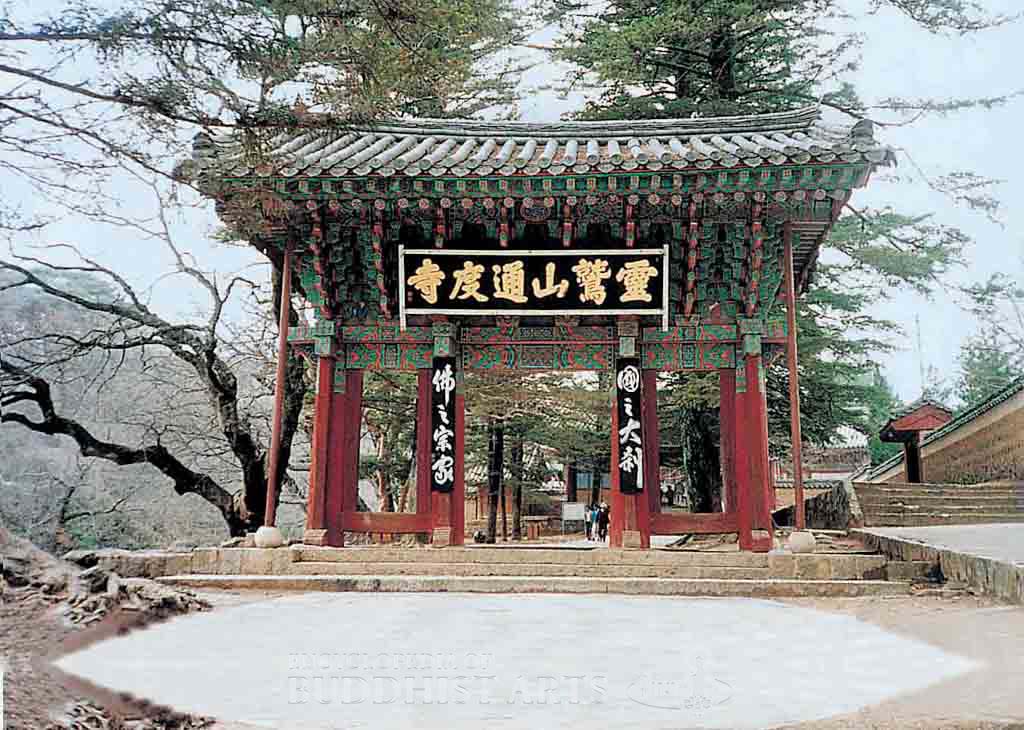

Tongdosa Temple: One Pillar Gate

Tongdosa Temple: Offering Bowl Stupa
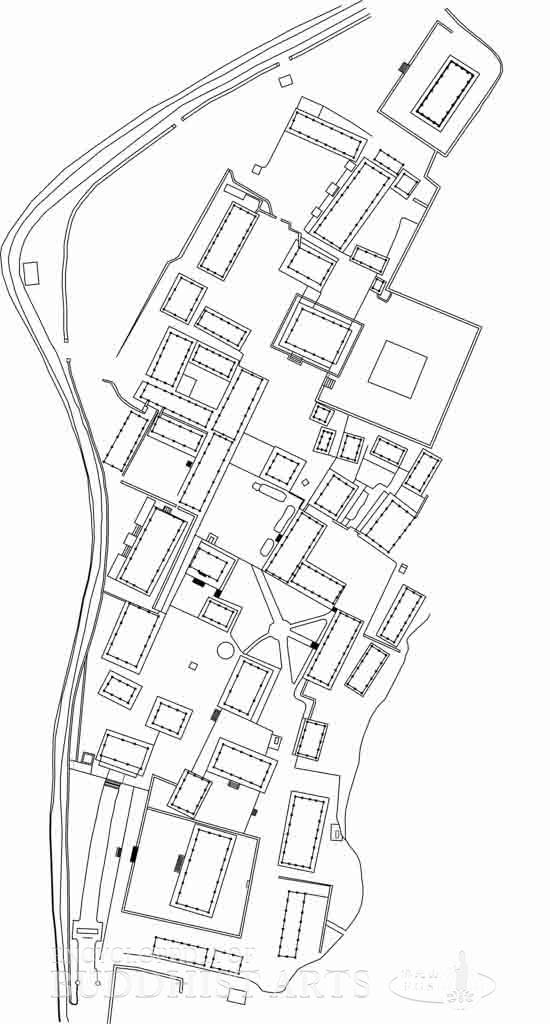
Tongdosa Temple (site layout)
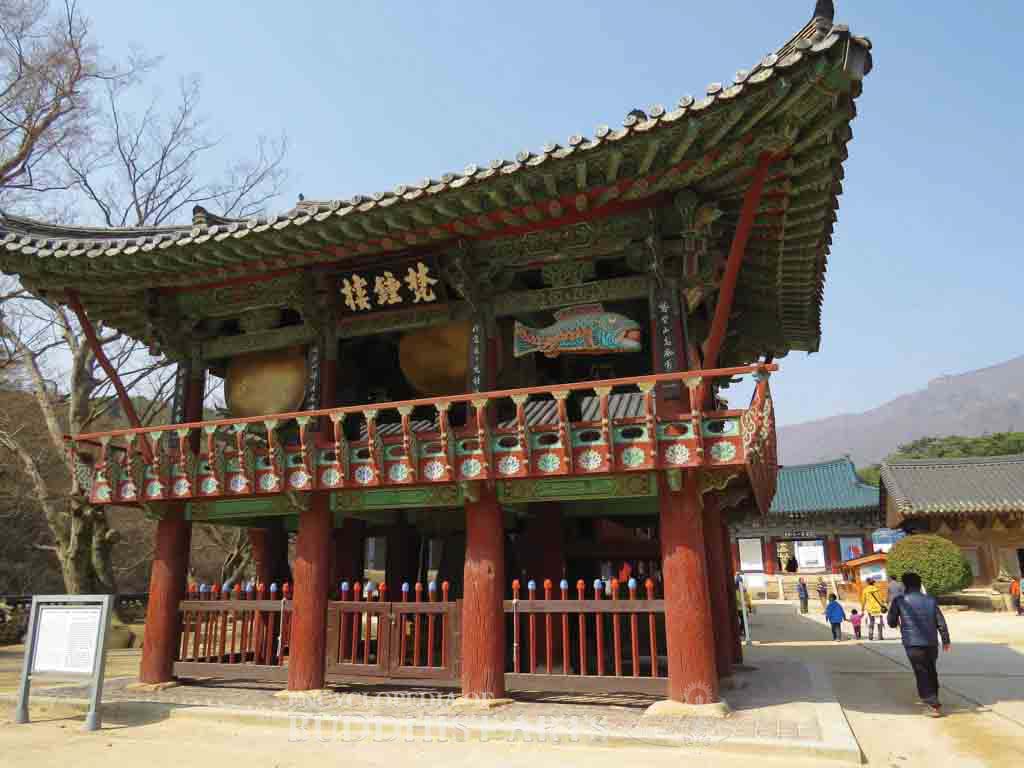

Tongdosa Temple: Bell and Drum Tower
Tongdosa Temple
SOUTH KOREA, South Gyeongsang, Yangsan
Tongdosa means Universal Deliverance Temple. It is one of the Three Major Temples in Korea and serves as the Head Temple for the 15th district of the Jogye order of Korean Seon Buddhism. According to the records, the temple was constructed in 646 during the Silla dynasty by Vinaya Master Jajang. It was built in order to house the Buddha relic, robe, and Tripitaka offered to him by an emperor from Tang dynasty China. Vinaya Master Jajang constructed a Vajra Ordination Platform in the temple, making Tongdosa the root temple for conferring monastic precepts. It was supported by the imperial family during the Unified Silla (668–935) and Goryeo (918–1392) dynasties, which made it the lead temple in the country. Most of the buildings were rebuilt in either 1601 or 1641 during the Joseon dynasty.
The main buildings are situated along the central axis, with subsidiary buildings and monastic quarters at the sides. The major structures include the One Pillar Gate, Heavenly King Gate, Great Hero Hall, Hall of Great Light, Vulture Peak Hall, Ultimate Bliss Hall, Dragon Flower Hall, Universal Light Hall, bell and drum tower, stone pagodas, stone lanterns, and a museum.
The temple is unusual in that there are no Buddha statues in the temple grounds. Instead, the temple courtyards are filled with stupas and pagodas that are said to house relics. Among the stone stupas in the temple, the Offering Bowl Stupa, located in front of Dragon Flower Hall, is considered unique. The lower and upper layers of the three-layer base are round, while the middle layer is in the form of a square pillar. The stupa body is in the shape of an alms bowl covered with a lid. It is listed as Treasure No. 471 in 1968.
The Tongdosa Museum, or Noble Treasures Museum, contains the richest collection of artifacts in terms of both quantity and quality. In particular, it houses over 600 Buddhist paintings, including the Eight Great Events from the Life of the Buddha and the illustration of the Avatamsaka Sutra, which were listed as Treasures No. 1041 and 1352 respectively.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture T-Z, page 1144.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture T-Z},
pages = 1144,
title = {{Tongdosa Temple}},
volume = 4,
year = {2016}}