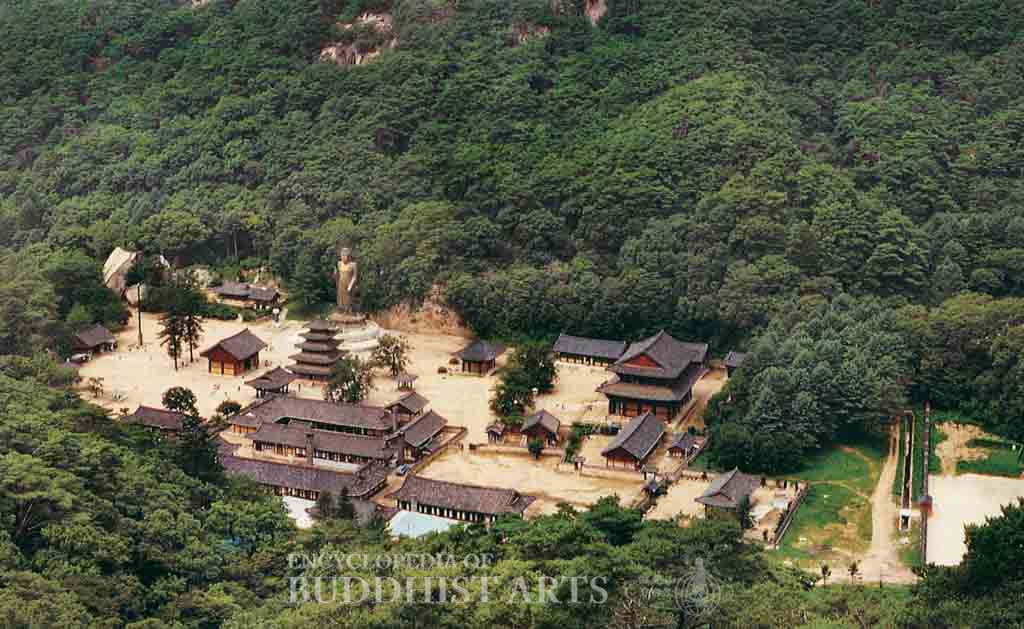

Beopjusa Temple (aerial view)
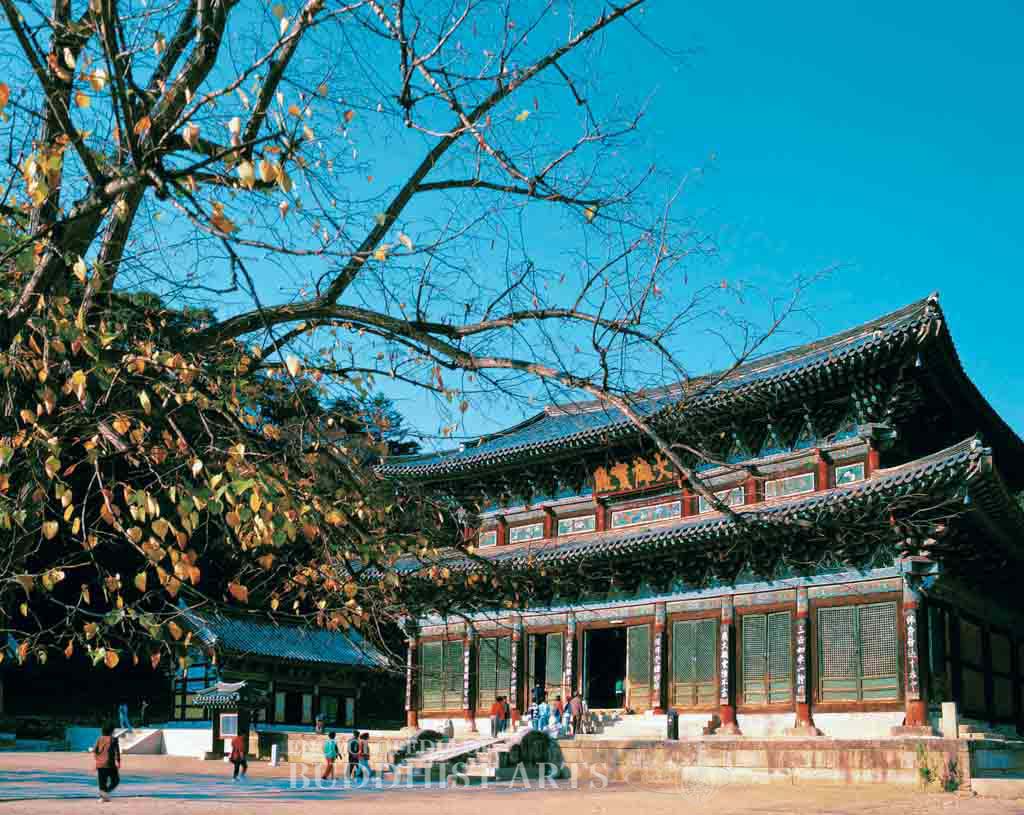

Beopjusa Temple: Great Hero Hall

Beopjusa Temple
Beopjusa Temple
SOUTH KOREA, North Chungcheong, Boeun
Beopjusa, which means Residence of the Dharma Temple, is one of the Five Major Temples in Korea. The temple was once a famous center for the Beopsang school. It is now the head temple for the 5th district of the Jogye order of Seon Buddhism. According to the records, the temple was founded by Master Uisin in 553 during the Silla dynasty. Master Uisin studied in India and brought back numerous sutras which he housed at this temple. During the Silla (57 BCE–935 CE) and Goryeo (918–1392) dynasties this temple received support from the royal families and underwent eight extensive reconstructions and expansions to become a compound with numerous halls and pagodas. The temple was completely destroyed during the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–1598). Most of the structures that remain today were rebuilt by Master Byeogam in 1624.
The temple compound, which occupies 1,922 ha, consists of over 60 buildings and 70 hermitages. The major structures include the One Pillar Gate, Diamond Gate, Heavenly King Gate, Great Hero Hall, Hall of Eight Pictures, Perfect Understanding Hall, Dragon Flower Hall, Patriarch Hall, and Great Bell Pavilion.
The seven-by-four bay Great Hero Hall, built upon a Sumeru platform, has a double-eave hip-and-gable roof. The roof is supported by a system of complex bracket sets. Colorful paintings can be found under the eaves. The hall houses seated statues of the Dharmakaya Buddha, Sambhogakaya Buddha, and Nirmanakaya Buddha. Each of these statues is about 5 m high. The hall was listed as Treasure No. 915 in 1987. The Hall of Eight Pictures is the only remaining five-tier wooden tower structure in Korea, and was listed as National Treasure No. 55 in 1962. The Perfect Understanding Hall, which contains a wooden statue of Avalokitesvara Bodhisattva, was listed as Treasure No. 916 in 1987.
Other state-recognized National Treasures and Treasures of the temple include the twin lion stone lantern, lotus-shaped stone basin, Four Heavenly Kings stone lantern, a seated Buddha rock carving, and a statue of Sudarsana Bodhisattva. In 1990 a 33 m high bronze statue of the Great Maitreya Buddha was installed next to the Dragon Flower Hall.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture A-F, page 70.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture A-F},
pages = 70,
title = {{Beopjusa Temple}},
volume = 1,
year = {2016}}