
Yongmunsa Temple
Yongmunsa Temple
SOUTH KOREA, Gyeonggi, Yangpyeong
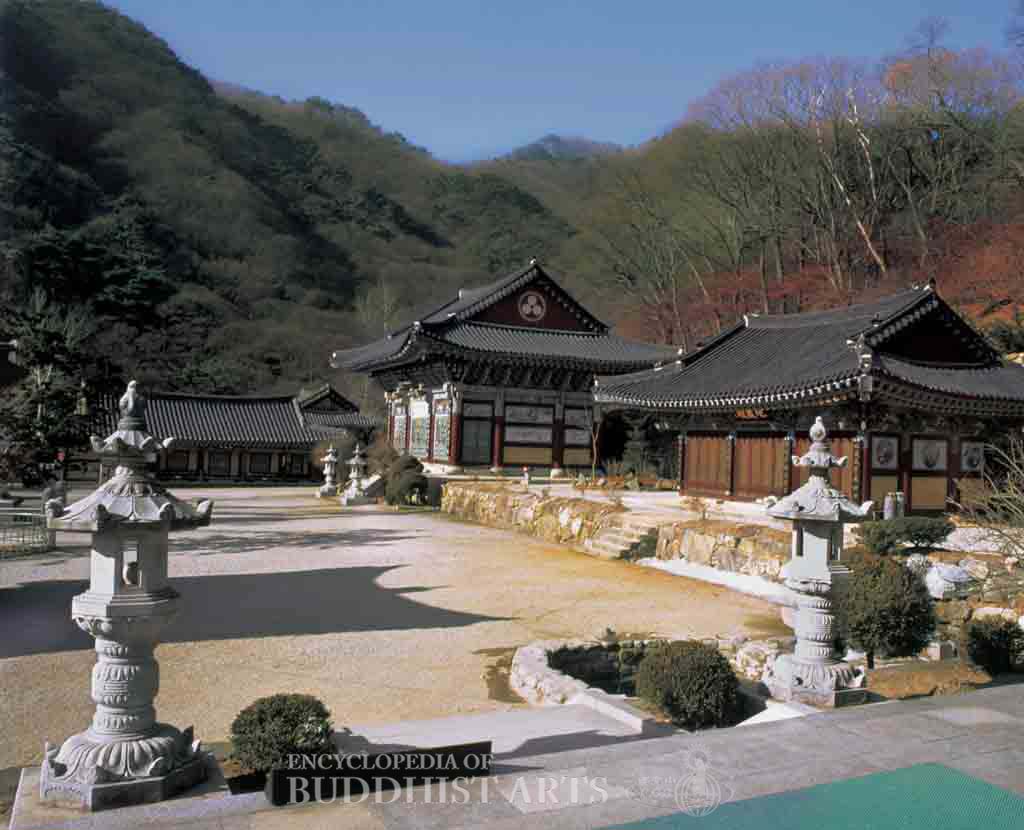
Yongmunsa, meaning Dragon Gate Temple, is a branch temple of Bongseonsa (Ancestral Offering Temple), which is the head temple for the 25th district of the Jogye order of Korean Seon Buddhism. The temple was established by Master Daegyeong in 913 during the Unified Silla dynasty. It was expanded and repaired in 1447, 1456, and 1480 during the Joseon dynasty. It suffered severe war damage twice, in 1907 and 1950, and was rebuilt each time. The present temple is the result of the reconstruction in 1958.
The main buildings include the Great Hero Hall, Ksitigarbha Hall, Mountain Spirit Shrine, bell tower, and Stupa of National Master Jeongji. Erected in the early Joseon dynasty (1392–1910), the stupa and its accompanying stele were listed as Treasure No. 531 in 1971.
Within the temple there is a famous gingko tree, which is said to have been planted at the end of the Silla dynasty (57 BCE–935 CE) by Prince Maui, the last crown prince. Now more than 1,100 years old, the tree was listed as Natural Monument No. 30 in 1971.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture T-Z, page 1357.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture T-Z},
pages = 1357,
title = {{Yongmunsa Temple}},
volume = 4,
year = {2016}}