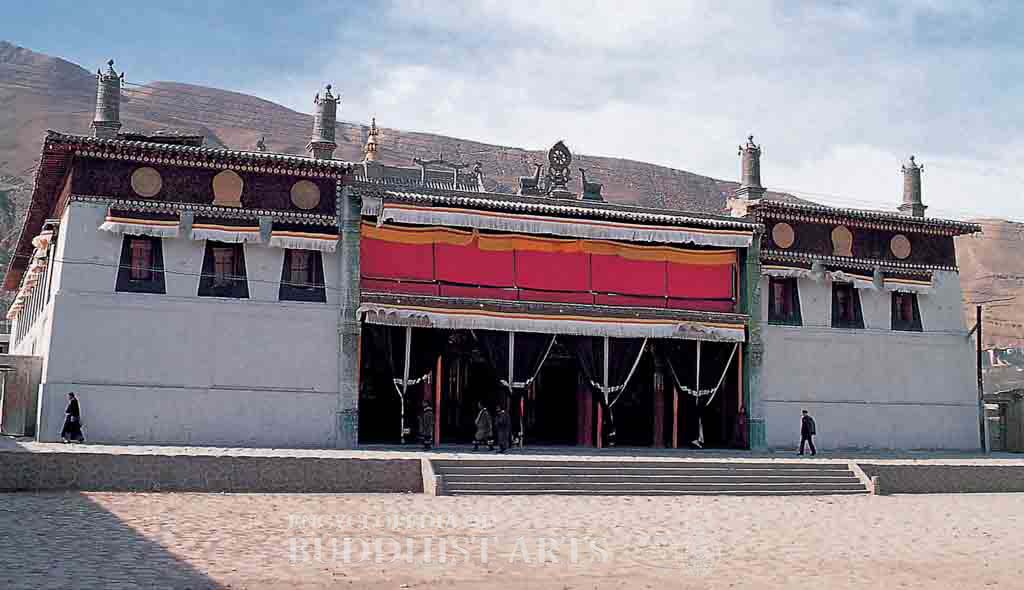

Rongwo Monastery: Central Hall
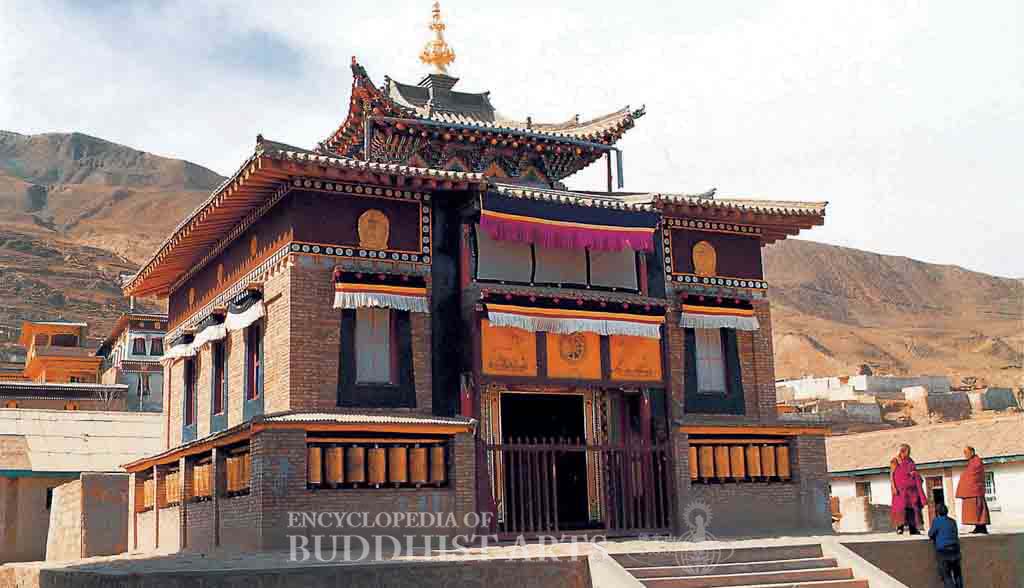

Rongwo Monastery: Stupa of the 7th Incarnate Lama
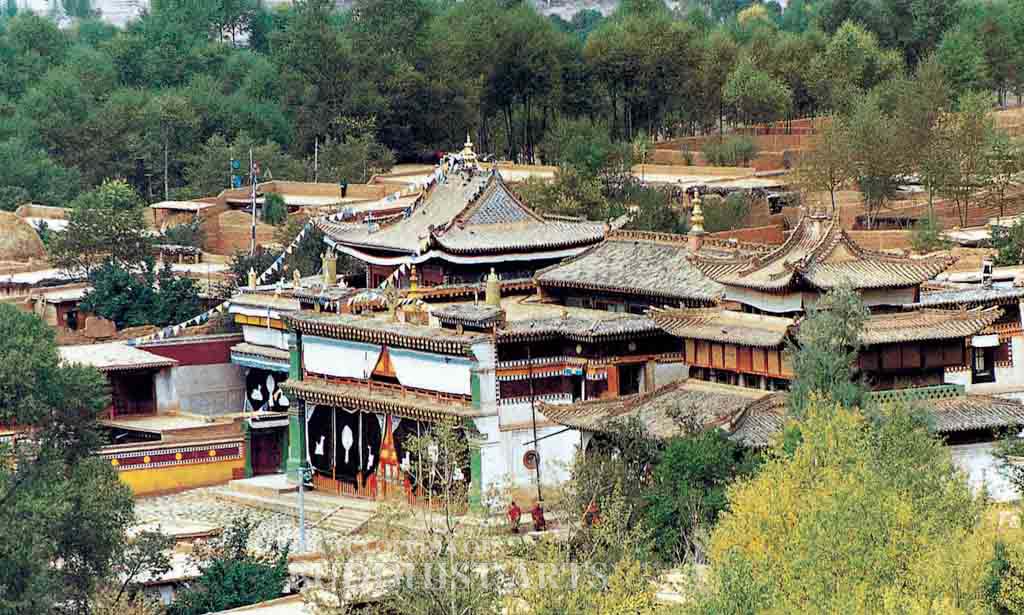

Rongwo Monastery: Wutun Lower Monastery
Rongwo Monastery
CHINA, Qinghai, Rebkong
The monastic complex consists of Rongwo Monastery and four subsidiary monasteries: Nyentok Monastery, Gomar Monastery, and the Wutun Upper and Lower Monasteries. The monastery was built on a small scale in 1301 during the Yuan dynasty and belonged to the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. It was reconstructed at the beginning of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) to form its current layout. During the rule of Emperor Chongzhen (reigned 1628–1644), it became a monastery of the Gelug school and the lineage of Shartshang Rinpoche was formed here. By the early Qing dynasty (1644–1911), there were more than 30 subsidiary monasteries. Currently there are four subsidiary monasteries which were built during the Ming dynasty. It was listed as a National Cultural Heritage Site in 1996.
In Rongwo Monastery the principal remaining buildings include the central hall, assembly hall, stupa of the 7th incarnate lama, sutra printing house, and the incarnate lama’s residence. In Nyentok Monastery the remaining buildings include the assembly hall, Maitreya Shrine, and Dharma Protector Hall. All that remains of the Gomar Monastery is an assembly hall, two Maitreya shrines of different sizes, and the Vajradhara Shrine. The Wutun Upper Monastery contains an assembly hall and the main temple gate, while the Wutun Lower Monastery of Wutun has a main temple gate and Maitreya Shrine. The buildings contain architectural features characteristic of Tibetan, Chinese, and Tibetan-Chinese styles, the latter being the most common. They constitute an integrated and harmonious style.
It was at this monastery that Rebkong art was founded. It is famous for its delicate paintings, statues, and embroidery. The monastery has a large number of cultural artifacts, such as gilt bronze, clay sculptures, wooden Buddha statues, colored paintings, thangkas, and Dharma instruments.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture M-S, page 900.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture M-S},
pages = 900,
title = {{Rongwo Monastery}},
volume = 3,
year = {2016}}