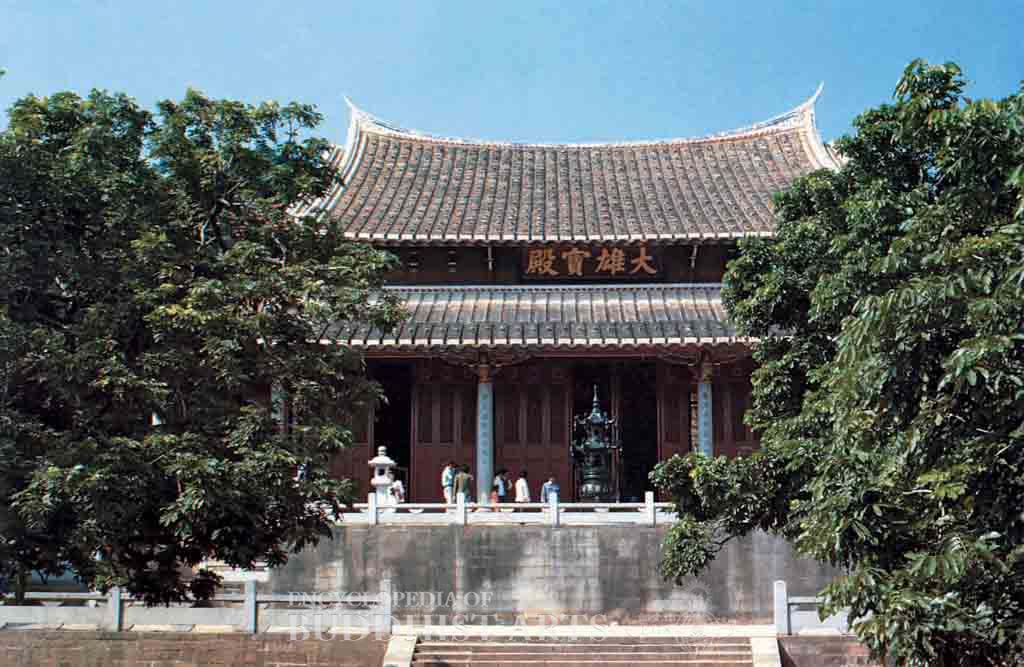

Guanghua Temple: Great Hero Hall
Guanghua Temple
CHINA, Fujian, Putian
Situated on Fenghuangshan (Phoenix Mountain), the temple was built in 558 during the Southern Dynasties. The temple was expanded a number of times until it reached the peak of its popularity during the Song dynasty (960–1279). However, most of the temple was destroyed during the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). The temple’s present buildings are from a Qing dynasty reconstruction modeled on the previous buildings. There were large-scale reconstructions in 1956 and 1980 and a Men’s Buddhist College was added. It was listed as a key Buddhist temple in the Han region of China in 1983.
The temple faces east and occupies more than 3 ha, with the buildings taking up 1.7 ha. The central axis is 385 m long with a screen wall, a gateway, main temple gate, Free Life Pond, Heavenly King Hall, Great Hero Hall, Dharma Hall, and the Patriarch Hall. The second story of the Dharma Hall is the sutra repository, and the second story of the Patriarch Hall is the Reclining Buddha Hall. There are two octagonal stone sutra pillars in front of the Heavenly King Hall. At the rear of the temple, on higher ground, there are the Avalokitesvara Pavilion and the Ksitigarbha Hall. To the east there is the Shijiawen Pagoda, which was built during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279). Standing on top a 2.7 m platform, the five-by-four bay Great Hero Hall has a double-eave hip-and-gable roof. The building is 22 m high and occupies 837 sq m. The post-and-tie beam timber structure inside are from the late Qing dynasty (1644–1911).
Four petal-shaped stone pillars at the back of the temple are remnants of the original Song dynasty structure. The octagonal sutra pillars were built in 1065 during the Northern Song dynasty, and are around 6 m high. One of the pillars is plain and does not contain any inscriptions, while the other has the Usnisavijaya Dharani Sutra engraved on it. There are also carvings of dragons, clouds, waves, upright lotuses, and Wisdom Kings on the base and spire of that pillar.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L, page 385.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture G-L},
pages = 385,
title = {{Guanghua Temple}},
volume = 2,
year = {2016}}