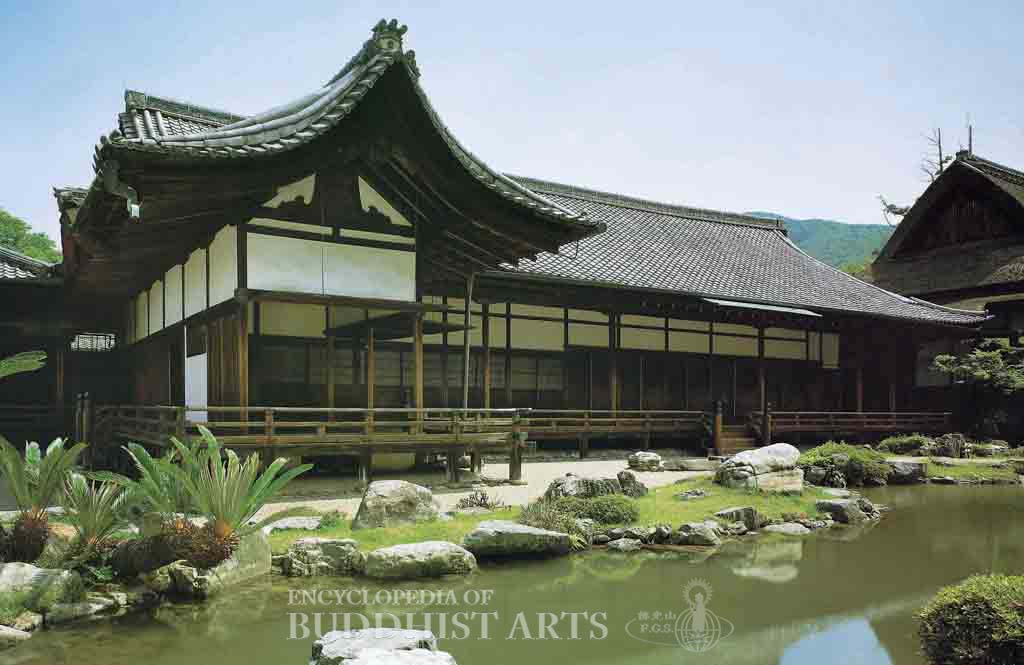

Sanboin Temple: Representative Building

Sanboin Temple: Representative Building (interior)
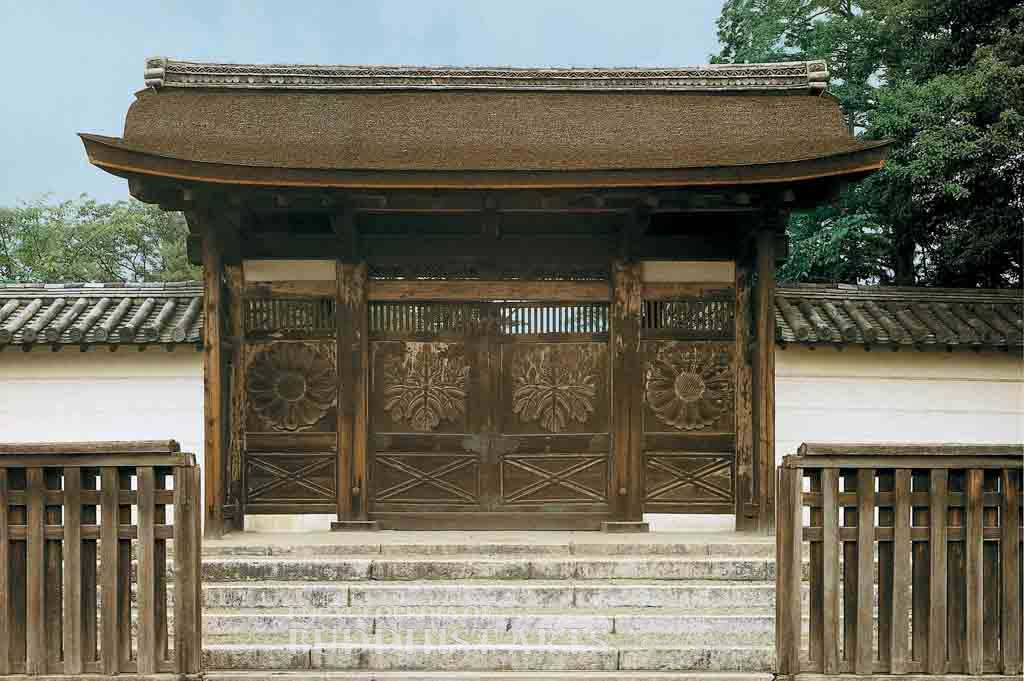

Sanboin Temple: Chinese Gate
Sanboin Temple
JAPAN, Kyoto, Fushimi
Sanboin Temple was established by Shokaku in 1115 during the Heian period as a branch of Daigoji Temple and was called Kongorinin. It was subsequently renamed Sanboin (House of the Three Treasures). In 1131, Toba Tenno ordered the construction of an initiation hall along with monastic quarters. Between 1200 and 1470 during the Kamakura period, the temple was damaged by four fires and each time it was restored by the abbot.
The current buildings include the Representative Building and Chinese Gate, both listed as National Treasures in 1954, along with the Imperial Hall, Pure Hall, and Homa Hall. The Representative Building was constructed in 1598 during the Azuchi-Momoyama period, when Toyotomi Hideyoshi went to see the gardens at Daigoji Temple. The twelve-by-five bay hall has a single-eave hip-and-gable roof covered with square wave tiles. The main entrance is extended into the garden with widely spaced columns. Inside there are lower, middle, and upper rooms with spaces divided by paintings, 40 of which have been listed as Important Cultural Properties.
The three-bay wide Chinese Gate with undulating bargeboards has a roof covered in cypress bark. The gate panels in the center have reliefs of the Toyotomi family emblem, while the panels on either side have chrysanthemum reliefs.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture M-S, page 928.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture M-S},
pages = 928,
title = {{Sanboin Temple}},
volume = 3,
year = {2016}}