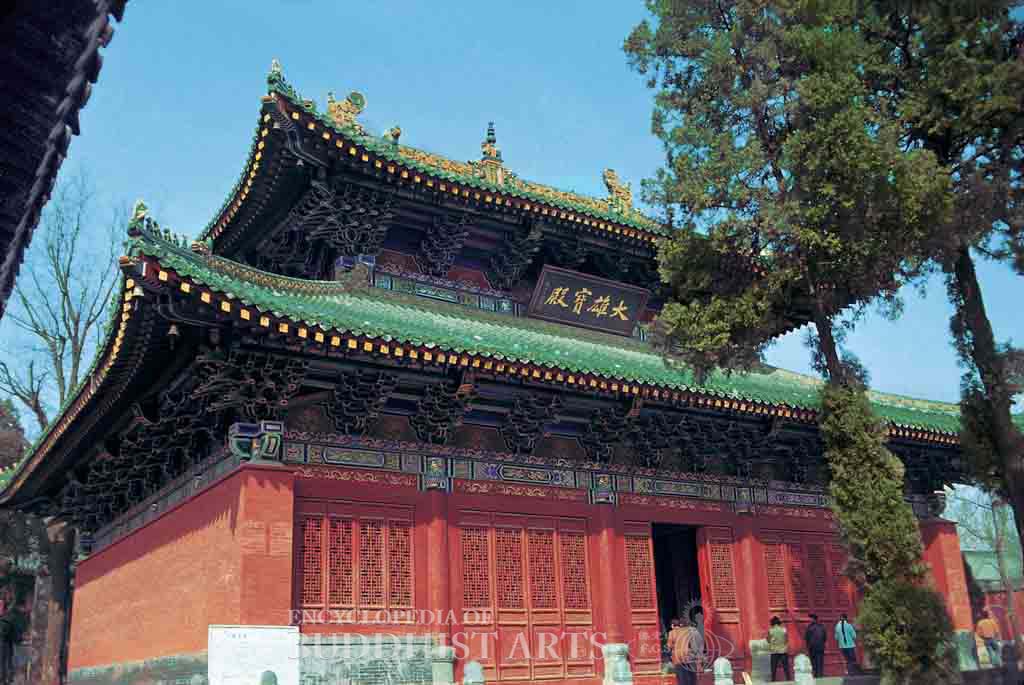

Shaolin Temple: Great Hero Hall
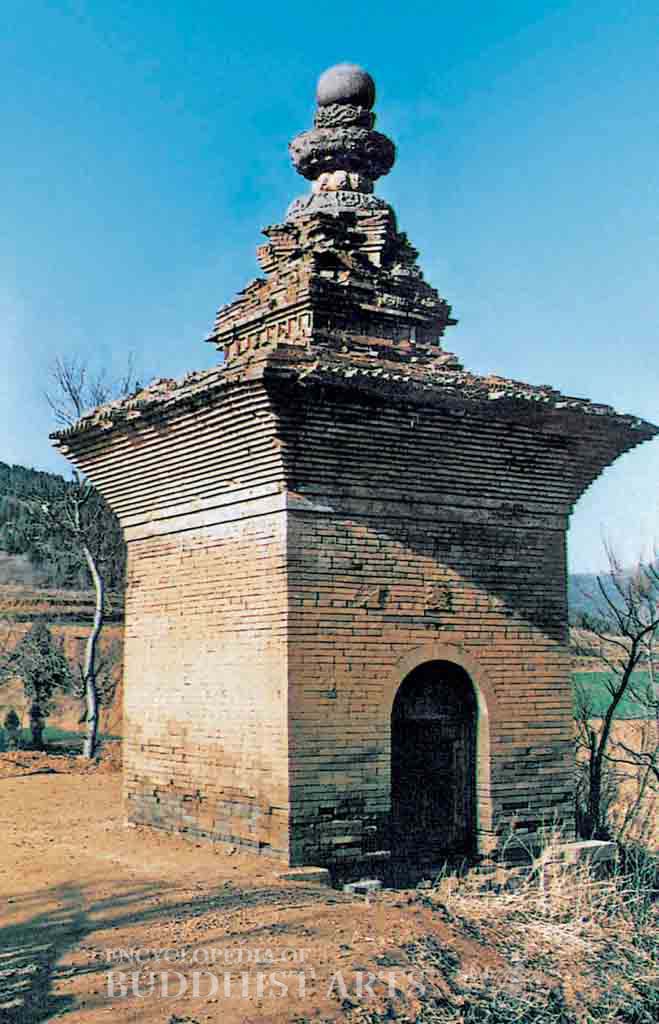

Shaolin Temple: Tongguang Pagoda
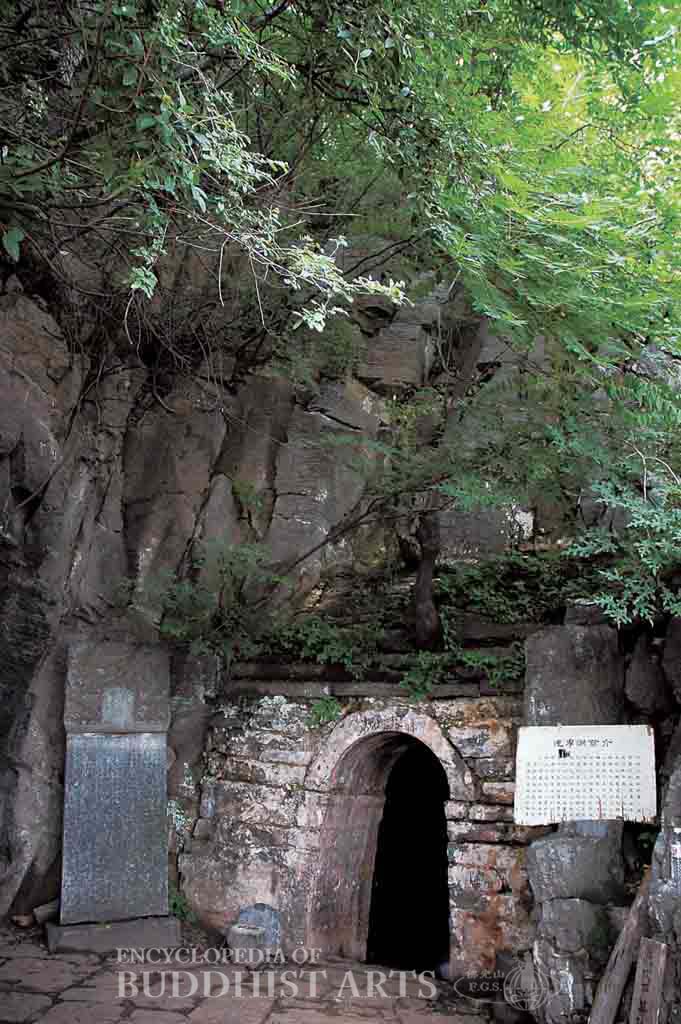

Shaolin Temple: Bodhidharma Cave
Shaolin Temple
CHINA, Henan, Zhengzhou
Shaolin refers to the grove at Shaoshishan Mountain, where the temple is located. It was built in 496 during the Northern Wei dynasty by order of Emperor Xiaowen (reigned 471–499) for Indian Master Buddhabhadra. Bodhidharma, the first patriarch of Chan Buddhism, sat in meditation at the temple for nine years. It is therefore recognized as the ancestral temple of Chan Buddhism. The temple was destroyed in 574 during the Northern Zhou dynasty’s persecution of Buddhism. It was rebuilt between 579 and 580. During the Sui dynasty (581–618) it became one of the largest Chan monasteries of northern China. During the early Tang dynasty (618–907), Li Shimin, the Prince of Qin, was assisted by the temple monks in defeating General Wang Shichong, which made the martial arts of the Shaolin monks famous. Throughout its history the temple has flourished and declined. It was damaged in wartime in 1928 and was rebuilt in 1949. It was listed as a key Buddhist temple in the Han region of China in 1983. As part of the Historic Monuments of Dengfeng, it was also listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2010.
The principal buildings include the main temple gate, Heavenly King Hall, Great Hero Hall, Dharma Hall, abbot’s quarters, Bodhidharma Pavilion, White Robe Hall, Ksitigarbha Hall, and Thousand Buddha Hall. About 300 m to the west of the temple there is a forest of pagodas, while 1 km to the west there is the First Patriarch Temple. Opposite the temple there is the Second Patriarch Temple on the Boyu Peaks. Bodhidharma Cave is in the Wuru Peaks, not far from the First Patriarch Temple. There are more than ten funerary pagodas dating back to the Tang dynasty that are scattered around the temple. These funerary pagodas include those of Chan Master Faru and Chan Master Tongguang.
The main temple gate was constructed in 1735 and repaired in 1974. Within the Thousand Buddha Hall there is a Ming dynasty (1368–1644) mural depicting the Five Hundred Arhats facing Vairocana Buddha. The Tongguang Pagoda was built in 771 during the Tang dynasty. It is a square pagoda built from polished bricks and yellow clay, and is 6.5 m high.
The temple houses numerous steles which were concentrated in the former Compassionate Cloud Hall. The building collapsed in 1984, at which time a veranda of steles was built. There are steles from various dynasties, starting with the Northern Qi dynasty (550–577). They have great historical value.
For more details, go to the Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture M-S, page 973.
Cite this article:
author = Hsingyun and Youheng and Johnson, Peter and Mankuang and Lancaster, Lewis,
booktitle = {Encyclopedia of Buddhist Arts: Architecture M-S},
pages = 973,
title = {{Shaolin Temple}},
volume = 3,
year = {2016}}